When we think of the healthcare industry, we often picture doctors, nurses, and cutting-edge medical equipment. However, there is a revolutionary technology that is quietly making waves in the medical field - 3D printing. This innovative technology has the potential to transform the way we approach healthcare, from personalized prosthetics to complex organ models. Let's delve into the world of 3D printing in healthcare and explore its impact on the medical industry.
The Evolution of 3D Printing in Healthcare
The use of 3D printing in healthcare is not a new concept, but its applications have expanded significantly in recent years. Initially, 3D printing was primarily used for creating anatomical models for surgical planning and medical education. However, with advancements in materials and technology, 3D printing has evolved to produce functional prosthetics, implants, and even human tissue.
Enhancing Patient Care with Personalized Solutions
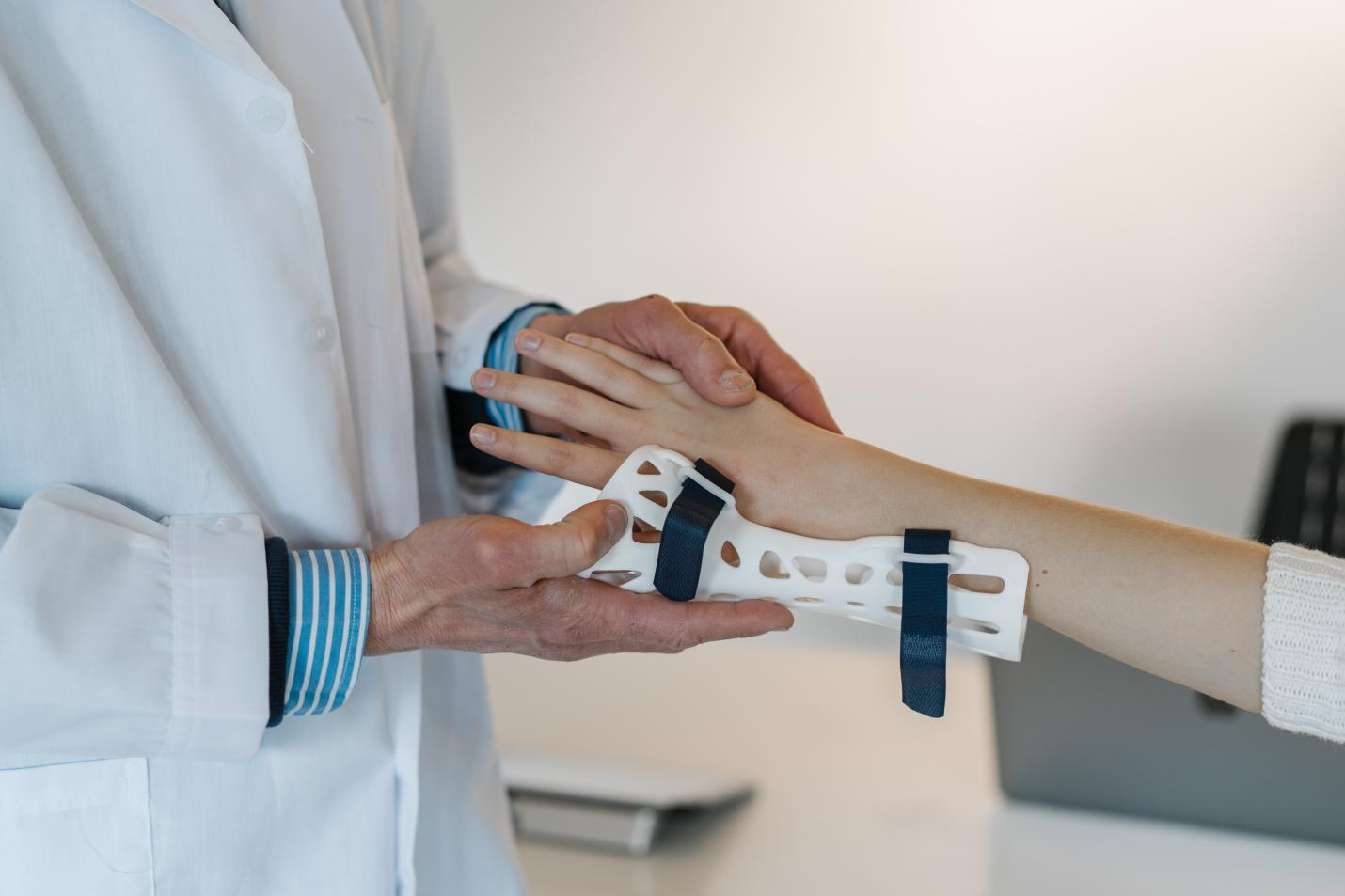
One of the most significant advantages of 3d printing in healthcare is the ability to create personalized solutions for patients. Traditional manufacturing methods often result in standard-sized medical devices and implants, which may not fit the unique anatomical requirements of every individual. With 3D printing, medical professionals can customize implants and prosthetics based on the patient's specific anatomy, leading to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Revolutionizing Surgical Procedures
3D printing has revolutionized surgical procedures by enabling surgeons to practice complex operations on patient-specific 3D printed models. These models allow surgeons to visualize the patient's anatomy in detail, identify potential challenges, and plan the surgery with precision. This technology has been particularly beneficial in intricate surgeries involving the spine, craniofacial structures, and organ transplants, where precision and accuracy are paramount.
The Future of 3D Printing in Healthcare
As 3D printing continues to advance, the possibilities for its application in healthcare are seemingly endless. Researchers are exploring the potential of bioprinting, a process that involves creating living tissue and organ constructs using 3D printing technology. While this technology is still in its early stages, the prospect of generating functional organs for transplantation could address the global organ shortage crisis and save countless lives.
Furthermore, the integration of 3D printing with other cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics holds promise for further enhancing patient care and medical innovation. From customized drug delivery systems to on-demand medical devices, the synergy of these technologies could shape the future of healthcare in unprecedented ways.
In conclusion, 3D printing is undeniably revolutionizing the healthcare industry, offering personalized solutions, improving surgical outcomes, and paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in medical science. As this technology continues to evolve, its impact on patient care and medical innovation will be profound, ushering in a new era of healthcare that is truly tailored to individual needs.







